Understanding Car Chargers and How They Work
Car chargers help you add power to your vehicle using electricity from a plug or a station. In this article, we explore different types of car chargers, how they connect to the car, and what makes each type useful for keeping your vehicle ready for trips and daily use.
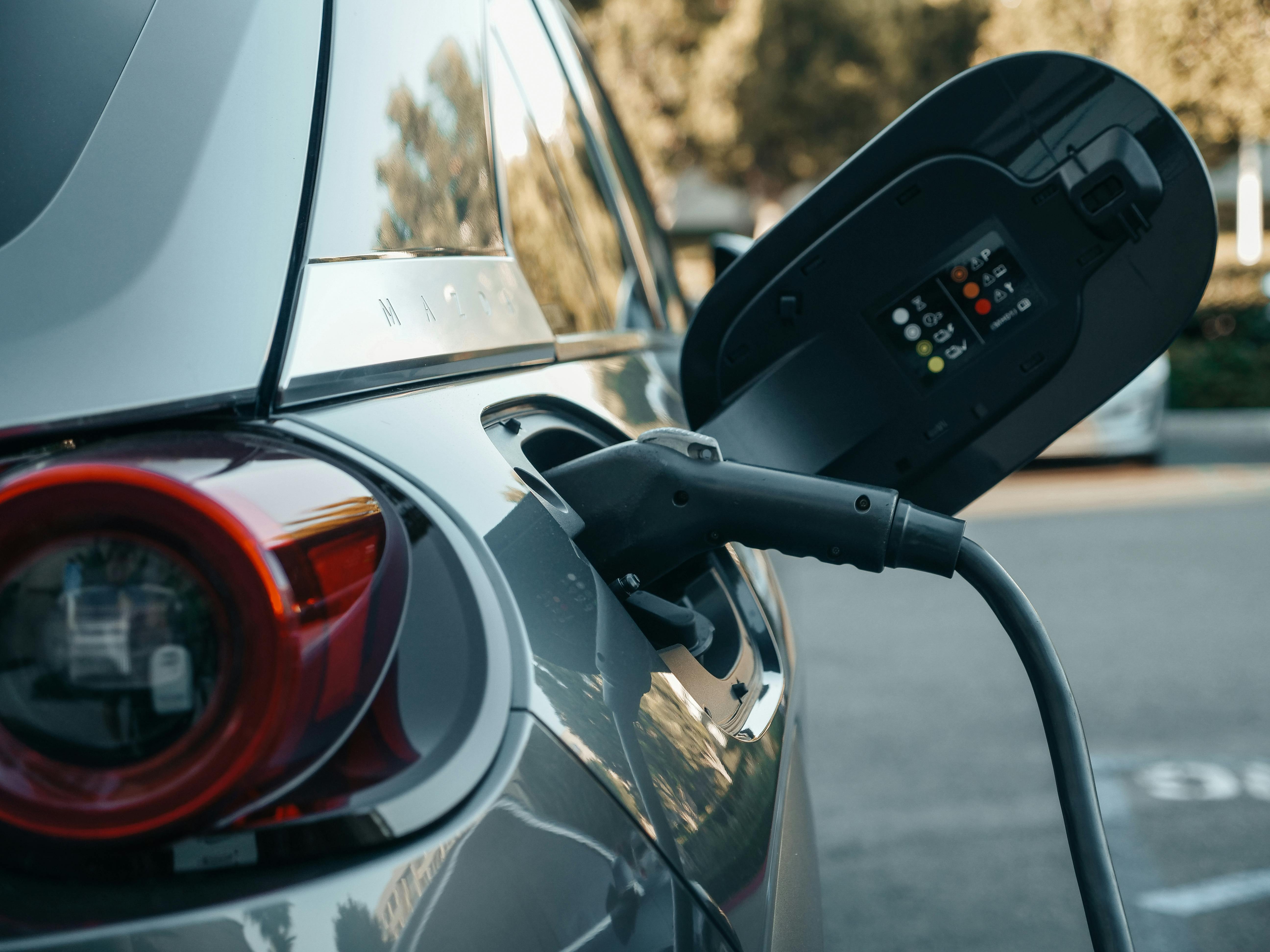

Types of Electric Vehicle Charging Systems
Electric vehicle charging systems are categorized into three main levels. Level 1 chargers use standard 120-volt household outlets, providing about 4-5 miles of range per hour of charging. Level 2 chargers operate on 240-volt circuits (similar to those used for clothes dryers) and deliver 10-60 miles of range per hour depending on the vehicle and charger specifications. Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, bypass the vehicle’s onboard charger to deliver high-power direct current, enabling 80% battery charge in as little as 30 minutes for compatible vehicles. These charging levels accommodate different scenarios, from overnight home charging to quick top-ups during long-distance travel.
How Car Charging Stations Function
Car charging stations convert standard electrical power into a form that electric vehicle batteries can efficiently use. When connected, the charging station first establishes communication with the vehicle through a control pilot signal that verifies proper connection and determines the maximum current available. The charger then delivers electricity at the appropriate voltage and current levels based on the vehicle’s requirements. Modern car charging stations incorporate RFID authentication, payment systems, and networking capabilities that enable users to locate stations, check availability, and process payments through smartphone applications. Public charging networks continue to expand, making EV charging increasingly convenient.
Vehicle Power Adapters for Different Charging Needs
Vehicle power adapters bridge compatibility gaps between different charging connectors and power sources. The most common connector types include J1772 (the North American standard for Level 1 and 2 charging), Combined Charging System (CCS), CHAdeMO, and Tesla’s proprietary connector. Adapters allow vehicles to use charging infrastructure designed for different connector standards. For example, non-Tesla vehicles can access Tesla destination chargers with appropriate adapters, while Tesla owners can use J1772 public stations with the adapter included with their vehicles. When traveling, having the right adapters ensures charging accessibility regardless of the available infrastructure.
Fast Car Chargers and Rapid Charging Technology
Fast car chargers employ advanced technology to significantly reduce charging times compared to standard options. These systems typically operate at 50-350 kW power levels, using liquid-cooled cables and sophisticated power electronics to safely deliver high currents. Fast charging stations feature advanced thermal management systems to prevent overheating during the charging process. While convenient for long trips, frequent use of fast chargers may affect battery longevity due to the heat generated during rapid charging. Most EV manufacturers recommend a balanced approach—using fast charging primarily for travel and relying on slower Level 2 charging for routine needs.
EV Home Chargers Installation and Requirements
Installing an EV home charger typically requires electrical modifications to support the higher power demands. Most residential EV chargers are Level 2 units requiring a 240-volt circuit with 40-50 amp capacity. Installation involves mounting the charging unit, running appropriate wiring, installing a dedicated circuit breaker, and sometimes upgrading the home’s electrical panel if it lacks sufficient capacity. Many utility companies offer rebates or incentives for home charger installation. Professional installation is highly recommended to ensure safety and code compliance, with costs typically ranging from $500 to $2,000 depending on the existing electrical infrastructure and complexity of installation.
Car Charger Technology and Pricing Considerations
The car charging market offers options across various price points and feature sets to accommodate different needs and budgets. Understanding these options helps consumers make informed decisions when investing in charging equipment.
| Charger Type | Typical Price Range | Charging Speed | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Portable | $200-$500 | 3-5 miles/hour | Portable, uses standard outlets, minimal installation |
| Basic Level 2 | $300-$700 | 12-25 miles/hour | Wall-mounted, simplified interface, basic safety features |
| Smart Level 2 | $500-$1,200 | 12-60 miles/hour | Wi-Fi connectivity, scheduling, usage tracking, app control |
| DC Fast Charger | $20,000-$100,000+ | 80% charge in 30-45 min | Commercial installation, complex cooling systems, high power |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Understanding Charging Efficiency and Power Management
Car chargers don’t transfer 100% of grid energy to the vehicle battery due to conversion losses. Level 1 and Level 2 chargers typically achieve 85-90% efficiency, while DC fast chargers range from 90-95% efficiency. Several factors affect charging efficiency, including cable quality, ambient temperature, and battery condition. Modern chargers incorporate smart power management features that optimize charging schedules to take advantage of lower electricity rates during off-peak hours. Some systems integrate with home energy management systems or solar installations, allowing EVs to charge primarily using renewable energy and even serve as backup power sources during outages.
The evolution of car charging technology continues to accelerate, bringing improved efficiency, faster charging speeds, and greater convenience to electric vehicle owners. As charging infrastructure expands and technology advances, the experience of charging an electric vehicle increasingly resembles the simplicity and convenience of filling a conventional vehicle with fuel, while offering additional benefits like home charging and potential integration with renewable energy sources.