How Wooden Houses Are Built and Used Around the World
Wooden houses are made using different types of wood and building methods. This article explains how walls, roofs, and floors are created, the variety of styles found in different countries, and how wood is shaped and joined to make strong, long-lasting homes.
Traditional Wooden House Construction Methods
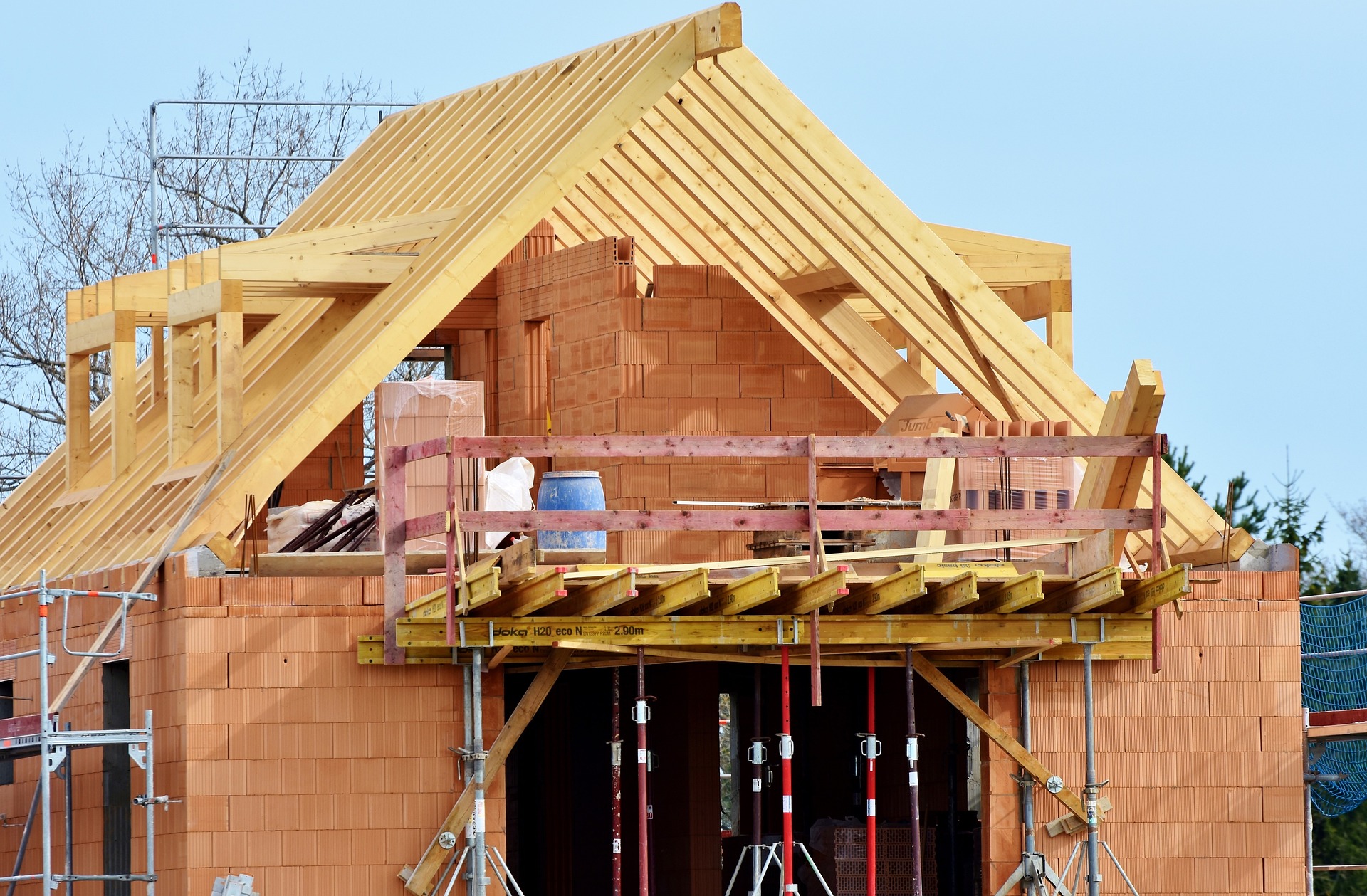
Wooden house construction varies significantly across regions, reflecting local timber availability, climate conditions, and cultural traditions. The log cabin technique, where horizontal logs are notched at the corners and stacked, remains iconic in North America and Northern Europe. In Scandinavia, the stavkirke (stave church) construction method uses vertical load-bearing posts with horizontal planks. Japanese minka houses employ complex joinery systems without nails, while timber framing in medieval European structures uses posts and beams with diagonal braces. Modern wooden house construction often incorporates engineered wood products like cross-laminated timber (CLT), glulam beams, and structural insulated panels that enhance strength while reducing material waste, allowing for greater design flexibility and taller wooden structures.
Types of Wooden Houses Around the World
Different regions have developed distinctive wooden house types adapted to local conditions. In North America, log cabins evolved from simple frontier shelters to sophisticated homes, while New England saltbox houses feature asymmetrical rooflines designed to withstand harsh winters. The Alpine regions showcase chalet-style homes with wide eaves and decorative carvings. In Russia and Eastern Europe, izba houses feature intricate decorative elements around windows and eaves. Southeast Asian stilted wooden houses provide protection from flooding and promote ventilation in humid climates. The Pacific Northwest’s indigenous peoples created plank houses from cedar, while Japan’s traditional minka farmhouses use complex wooden joinery systems. Each type represents cultural adaptations to available materials, climate challenges, and aesthetic traditions, creating a rich global tapestry of wooden architecture.
Modern Wooden House Designs and Innovations
Contemporary wooden house designs blend traditional techniques with cutting-edge technology and sustainability principles. Architects now utilize mass timber construction, including cross-laminated timber panels that allow for multi-story wooden buildings with strength comparable to concrete. Prefabricated wooden houses have gained popularity, with components manufactured in controlled factory settings for precision, reduced waste, and faster on-site assembly. Passive house design principles are increasingly incorporated into wooden homes, maximizing energy efficiency through strategic orientation, superior insulation, and airtight construction. Modern wooden house designs often feature open floor plans with large glass facades that create a dialogue between interior spaces and natural surroundings. These innovations maintain wood’s traditional warmth while adding contemporary aesthetics, environmental performance, and structural capabilities.
Environmental Benefits of Wooden Houses
Wooden houses offer significant environmental advantages compared to concrete or steel construction. Timber is a renewable resource when harvested sustainably, with managed forests continuously replanting trees. Wood acts as a carbon store, sequestering carbon dioxide absorbed during tree growth and keeping it locked away for the building’s lifetime. The production process for wooden building materials typically requires less energy than manufacturing concrete or steel, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Well-designed wooden houses provide natural insulation, potentially reducing heating and cooling demands. At the end of their lifecycle, wooden building components can be repurposed, recycled, or naturally decomposed, unlike many synthetic building materials. These environmental benefits have driven increased interest in wooden construction as architects and homeowners seek more sustainable building solutions.
Cultural Significance of Wooden Homes Around the World
The wooden house holds profound cultural significance across diverse societies worldwide. In Finland, the traditional wooden sauna represents not just a building but a central element of national identity and social ritual. Japan’s wooden architecture embodies philosophical principles of impermanence and harmony with nature through its joinery techniques and relationship to surrounding landscapes. In Norway, the stave churches showcase intricate wooden craftsmanship that blends pagan and Christian symbolism. Russia’s ornate wooden houses with decorative window frames (nalichniki) tell stories through carved symbolic patterns. The Pacific Northwest’s indigenous peoples incorporated clan symbols and creation stories into their wooden dwellings. These cultural expressions in wooden architecture represent accumulated knowledge, aesthetic values, and worldviews passed down through generations of builders, creating structures that transcend mere shelter to become repositories of cultural identity.
Economic Aspects of Wooden House Construction
Wooden house construction costs vary significantly based on design complexity, material selection, location, and labor markets. Basic timber frame construction typically ranges from $150-$250 per square foot, while custom-designed wooden homes with premium finishes may exceed $350 per square foot. Prefabricated wooden house kits can reduce costs to $100-$150 per square foot but may require additional site preparation and assembly expenses. Log homes generally cost 20-30% more than conventional construction due to specialized materials and labor requirements.
| Construction Type | Average Cost (per sq ft) | Maintenance Considerations | Typical Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Log Home | $150-$350 | Regular staining/sealing | 100+ years |
| Timber Frame | $200-$400 | Minimal wood treatment | 150+ years |
| Prefab Wooden Kit | $100-$200 | Depends on materials used | 50-100 years |
| CLT Construction | $250-$400 | Low maintenance | 100+ years |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Wooden houses typically have higher initial construction costs compared to conventional building methods but often provide long-term savings through energy efficiency, durability, and lower maintenance when properly constructed. In regions with abundant timber resources, local wood can reduce transportation costs and support regional economies. The growing market for sustainable buildings has also increased the resale value of well-built wooden homes in many markets.
Maintenance and Longevity of Wooden Houses
Proper maintenance is essential for preserving wooden houses and ensuring their longevity. Regular inspection for moisture intrusion, insect damage, and decay allows for early intervention before structural issues develop. Exterior wooden surfaces require periodic treatments with appropriate preservatives, stains, or paints to protect against ultraviolet damage and moisture. Maintaining good ventilation throughout the structure prevents condensation that can lead to mold growth and wood deterioration. Despite maintenance requirements, well-constructed wooden houses demonstrate remarkable durability, with examples of timber structures surviving for centuries across various climates. The Norwegian stave churches dating back to the 12th century and Japan’s Horyuji Temple (built in 607 CE) showcase wood’s potential longevity when properly maintained. Modern preservative treatments, careful design details that protect wood from prolonged moisture exposure, and regular maintenance schedules help contemporary wooden houses achieve similar lifespans while maintaining their beauty and structural integrity.